Stainless Steel Grade
Chemical Composition of Duplex
| UNS | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Cu | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S32101 | 0.04 | 4.0-6.0 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | 21-22 | 1.35-1.7 | 0.1-0.8 | 0.2-0.25 | 0.1-0.8 | |
| S32304 | 0.03 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | 21.5-24.5 | 3-5.5 | 0.05-0.6 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.05-0.6 | |
| S31803 | 0.03 | 2 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1 | 21-23 | 4.5-6.5 | 2.5-3.5 | 0.08-0.2 | ||
| S32205 | 0.03 | 2 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1 | 22-23 | 4.5-6.5 | 3.0-3.5 | 0.14-0.2 | ||
| S32750 | 0.03 | 1.2 | 0.035 | 0.02 | 0.8 | 24-26 | 6.0-8.0 | 3.0-5.0 | 0.24-0.32 | 0.5 | |
| S32760 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 1 | 24-26 | 6.0-8.0 | 3.0-4.0 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.5-1.0 | W:0.5-1.0 |
Physical Properties of Duplex
| UNS | Yield Strength (MPa, min) | Tensile Strength (MPa, min) | Elongation (%, min) | Hardness (BRINELL, max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S32101* | 450 | 650 | 30 | 290 |
| S32304 | 400 | 600 | 25 | 290 |
| S31803 | 450 | 620 | 25 | 293 |
| S32205 | 450 | 655 | 25 | 293 |
| S32750 | 550 | 795 | 15 | 310 |
| S32760 | 550 | 750 | 25 | 270 |
| Austenitic 300 Series | ||||
| S30400 | 205 | 515 | 40 | 201 |
| S31603 | 170 | 485 | 40 | 217 |
PRE Comparison of Stainless Steels
| Common Name | UNS | PRE |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | S30400 | 18 |
| 316L | S31603 | 24 |
| 904L | N08904 | 32 |
| 254SMO(6% Mo) | S31254 | 41 |
| Alloy 825 | N08825 | 28 |
| LDX2304 | S32304 | 22 |
| DX2205 | S31803 | 34 |
| SDX2507 | S32750 | 38 |
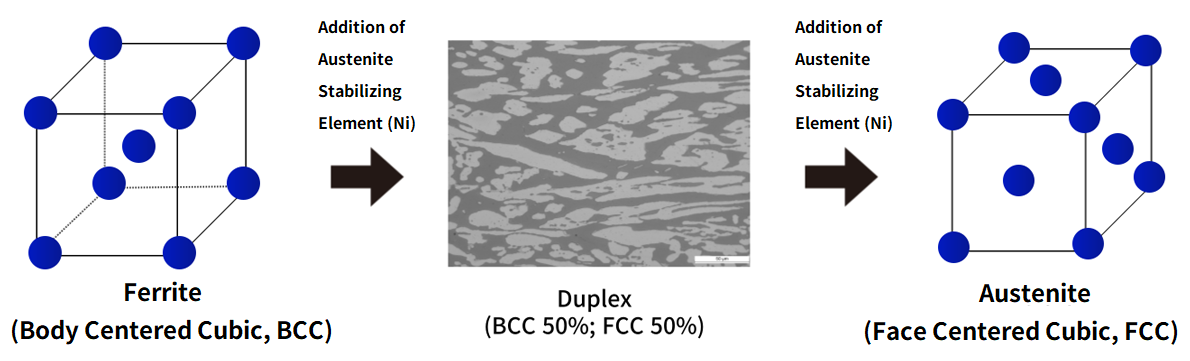
Duplex can theoretically be composed with a ratio of 30% - 70% ferrite or austenite phase. Actual duplex is composed of almost equal proportions (50:50) of ferrite and austenite phases. Since ferrite and austenite phases have different physical properties, combining them in appropriate proportions is the key to duplex production.
Just as chromium carbides precipitate in the sensitization range in austenitic steel, duplex can also precipitate compounds such as Sigma Phase and Chi Phase that inhibit physical properties in the ferrite phase at high temperatures. Since nitrogen addition significantly delays such compound precipitation, nitrogen is a very important element in duplex composition.
1) Chromium (Cr): In stainless steel, chromium of 10.5% or more forms a passive film to help prevent steel oxidation. As the amount of chromium increases, resistance to corrosion increases. Chromium is one of the ferrite stabilizing elements, and as the amount of chromium increases, the tendency for iron (Fe) to transform into a body-centered cubic structure (BCC) increases. Therefore, for duplex or austenitic steel composition, the amount of nickel, an austenite stabilizing element, must also increase as chromium increases. Typically, duplex contains 16-20% chromium.
2) Molybdenum (Mo): Molybdenum, one of the ferrite stabilizing elements, is an element that provides strong resistance to pitting corrosion. In stainless steel with 18% or more chromium, molybdenum addition can improve pitting resistance by about 3 times compared to chromium. Since molybdenum also has strong resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride atmosphere, it is one of the very important elements for duplex corrosion resistance. However, since molybdenum can contribute to unnecessary compound precipitation in the ferrite phase, molybdenum content in duplex is limited to about 4%.
1) Nitrogen (N): As an austenite stabilizing element, when added, it provides strong resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion of steel and significantly increases the strength of steel. Since it is also an austenite stabilizing element, it is partially used as a substitute for relatively expensive nickel in duplex. Since it delays unnecessary compound precipitation time, it is used in austenitic and duplex as a Sigma Phase precipitation prevention element. Since it also has the effect of solid solution hardening, it greatly helps improve strength.
2) Nickel (Ni): As a representative austenite stabilizing element, it changes the grain structure of steel from body-centered cubic structure (BCC) to face-centered cubic structure (FCC). Duplex contains 1.5-7% nickel, and like nitrogen, it inhibits unnecessary compound precipitation in the ferrite phase. Since the austenite phase has advantages in improving physical properties such as toughness, nickel and nitrogen are very important elements for improving the physical properties of duplex.



