Stainless Steel Grade
Corrosion refers to the change in steel properties due to the influence of chemical atmosphere or temperature. Duplex has stronger corrosion resistance than general austenitic steel in most chemical atmospheres. The resistance of duplex in various types of corrosive atmospheres is introduced in more detail below.
All duplexs have corrosion resistance in diluted sulfuric acid atmosphere compared to 304L and 316L.
Especially in contaminated sulfuric acid atmosphere such as FGD Scrubber, duplex shows stronger corrosion resistance compared to austenitic steel.
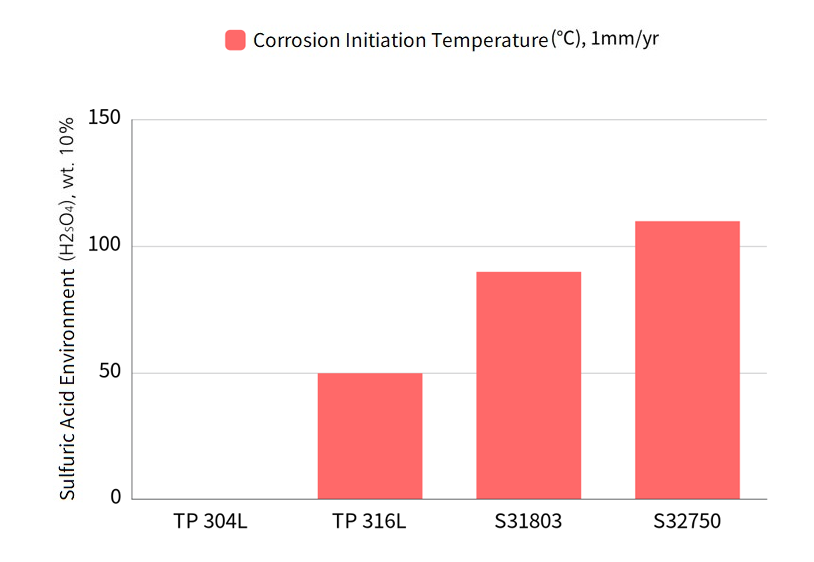
Comparison of corrosion occurrence temperature in 10% sulfuric acid mixture (TP304L corrodes below 0°C)

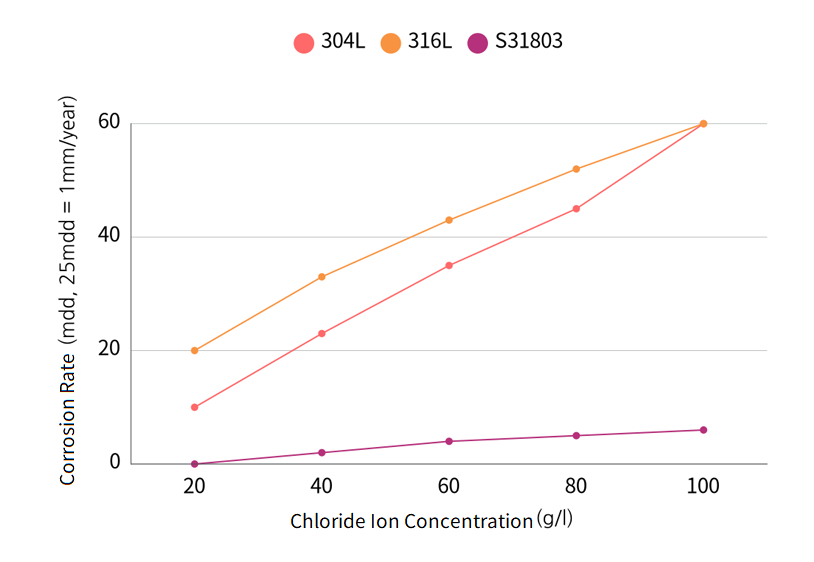
Corrosion rate comparison in FGD scrubber
In strong hydrochloric acid atmosphere, most stainless steels are vulnerable to corrosion. In diluted hydrochloric acid atmosphere, super duplex has corrosion resistance similar to nickel steel Alloy 28 or super austenitic series steel. In 3% diluted hydrochloric acid atmosphere, super austenitic steel S32760 has corrosion resistance below 80°C.
In nitric acid atmosphere, chromium strengthens corrosion resistance while molybdenum content makes steel corrosion resistance vulnerable. Molybdenum content within 2% is recommended, and lean duplex series show strong corrosion resistance. Since it shows corrosion resistance similar to basic austenitic steel of 300 series, duplex use is not recommended.
White liquor used in Kraft Process for paper production is a strongly alkaline solution mainly composed of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide. White liquor has considerable caustic corrosiveness, and duplex shows very strong corrosion resistance to white liquor compared to 300 series austenitic steel. Therefore, duplex has been very frequently used in pulp production processes since its initial development. In addition, it can be used in food processes, clothing manufacturing processes, soap and cleaner manufacturing processes, pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, etc. where caustic soda solution is used.
Corrosion rate comparison when using White Liquor
Phosphoric acid itself is not corrosive, but it becomes corrosive when mixed with substances such as chlorides or fluorides in industrial processes. Duplex has stronger corrosion resistance than austenitic steels in the above mixture atmosphere.
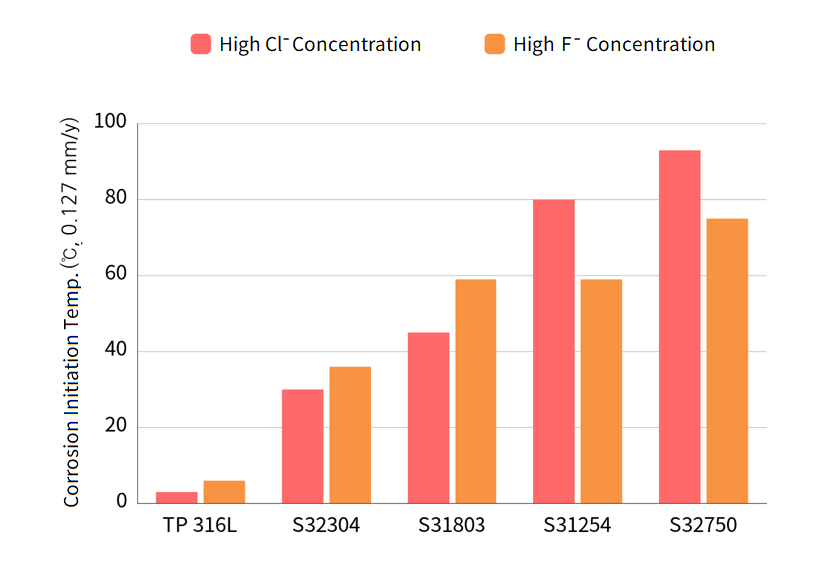
Corrosion comparison by steel grade in Wet Phosphoric Acid + Chloride/Fluoride
Standard duplex and super duplex show great corrosion resistance to organic acid mixtures. Especially super duplex S32750 shows perfect corrosion resistance even at the boiling point temperature of acetic acid and formic acid mixture, which is one of the strongest organic acids. Super duplex is perfectly suitable for use in organic acid manufacturing processes such as terephthalic acid used in polyester and PET resin manufacturing.
Pitting corrosion is a type of localized corrosion in which small holes randomly appear on the metal surface. Scientists experimentally discovered that the most important elements for defending against pitting corrosion in alloys are chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen, and formulated this to present guidelines for preventing pitting corrosion during design. This formula is called PRE (Pitting Resistance Equivalents) and can be calculated as follows.
PRE = %Cr + 3.3 x (%Mo + 0.5 x %W) + 16 x %N
Duplex has stronger resistance to crevice corrosion than austenitic steel, just like pitting corrosion. When duplex and austenitic steel are among the options and have similar PRE, it is desirable to use duplex because of its high strength and economy. For example, if considering the use of super duplex and super austenitic steel, super duplex is recommended unless the atmosphere is exposed to high temperatures of 250°C or higher for a long time, or resistance to low-temperature impact strength below 50°C is required.
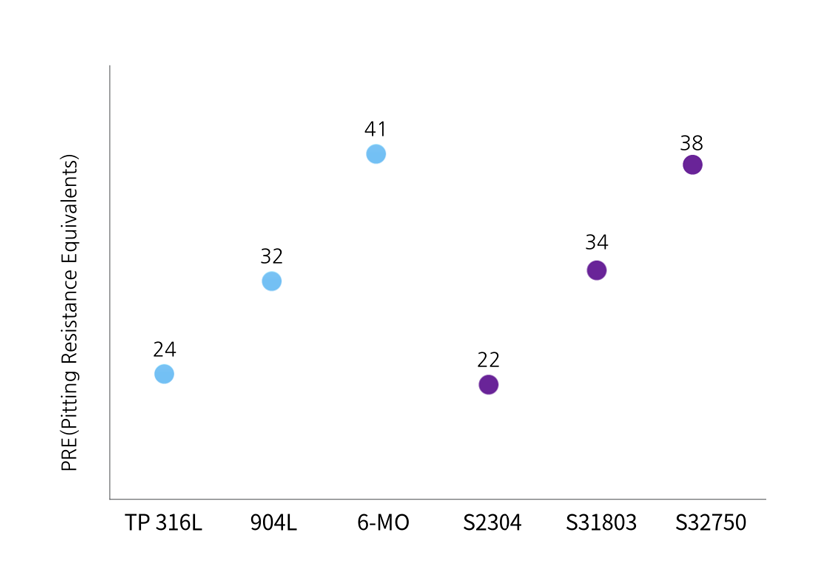
PRE comparison of austenitic steel and duplex
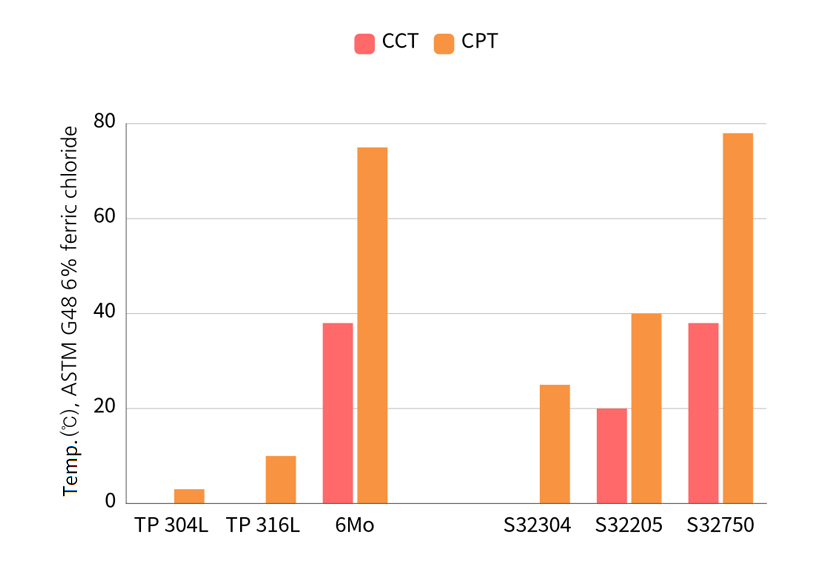
CCT (Critical Crevice Temperature) / CPT (Critical Pitting Temperature) comparison
Duplex is known to be strong against stress corrosion cracking (SCC) in environments with chloride and sulfide atmospheres. Therefore, it has been steadily used in chemical and petroleum refining industries where chloride and sulfide atmospheres exist. Stress corrosion cracking can occur due to environmental conditions such as high temperature, high chloride concentration atmosphere, hydrogen-induced cracking, etc., but it is generally stronger against stress corrosion cracking than austenitic steel.



